Notes on DCMI specifications for expressing Dublin Core™ metadata in RDF
Notes on DCMI specifications for Dublin Core™ metadata in RDF
| Creator: |
Mikael
Nilsson KMR Group, NADA, KTH (Royal Institute of Technology), Sweden Thomas Baker DCMI |
|---|---|
| Date Issued: | 2006-05-30 |
| Identifier: | http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dc-rdf-notes/2006-05-29/ |
| Replaces: | Not applicable |
| Is Replaced By: | Not applicable |
| Latest Version: | http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dc-rdf-notes/ |
| Description of Document: | This document serves as a guide to implementers to the changes introduced with the 2006-05-29 Working Draft "Expressing Dublin Core™ metadata using the Resource Description Framework (RDF)". |
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Background
- Support for domains and ranges
- Support for value strings
- Deprecated constructs
- Other changes
- References
1. Introduction
In May 2006, DCMI released for public comment the Working Draft "Expressing Dublin Core™ metadata in the Resource Description Framework (RDF)" [DC-RDF]. Subject to public review and discussion in the context of DCMI process, the May 2006 Working Draft is intended eventually to replace two legacy DCMI documents:
- Expressing Simple Dublin Core™ in RDF/XML [DCMES-XML], a DCMI Recommendation from July 2002;
- Expressing Qualified Dublin Core™ in RDF / XML [DCQ-RDFXML], a DCMI Proposed Recommendation from May 2002.
This document provides a guide to the changes introduced with the May 2006 Working Draft. DCMI is seeking comments from communities affected by these differences. The content of any future DCMI Recommendation based on the May 2006 Working Draft will depend on feedback received from these communities.
2. Background
Since 1997, the "Dublin Core™ data model" has evolved in a process of mutual influence with W3C's Resource Description Framework (RDF). This process has resulted in the DCMI Abstract Model[ABSTRACT-MODEL], which was published in March 2005 as a DCMI Recommendation. The DCMI Abstract Model now provides a reference model on the basis of which particular Dublin Core™ expressions can be defined.
Since the publication of the DCAM, the DC RDF task force of the Architecture WG has been preparing a new expression of Dublin Core™ in RDF. In March 2006, the DCMI Directorate awarded a contract to Mikael Nilsson (Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden) for finalizing and preparing for publication the existing draft produced within the DC RDF task force.
The new specification represents a significant step in the evolution of the Dublin Core™ RDF expressions. Historically, Dublin Core™ metadata expressed in RDF has suffered from a number of problems, including:
-
the existence of two legacy expressions of Dublin Core™ metadata in RDF [DCMES-XML,DCQ-RDF-XML];
-
conflicting recommendations in the above documents regarding the use of literal strings in Dublin Core™ metadata;
-
implementation complexity due to the use of idiosyncrasic constructs;
-
difficulties in providing formal ranges and domains for Dublin Core™ properties.
The legacy RDF expressions, which predate the DCAM, contain constructs that are incompatible with concepts in the DCAM.
The May 2006 specification addresses these problems in ways described below.
3. Support for domains and ranges
The most significant change introduced by the May 2006 Working Draft is the addition of support for domains and ranges of properties in general, and of DCMI-defined properties in particular. DCMI metadata terms have hitherto been defined exclusively in natural language; the RDF expression of the DCMI term set (e.g., http://dublincore.org/2003/03/24/dces) served essentially to convey these English-language definitions in a form ingestable by RDF applications. As part of the process of clarifying the RDF expression for Dublin Core™ metadata, it has become evident that DCMI would benefit from supplementing these English-language definitions with machine-understandable declarations of domains and ranges. Such additional, machine-understandable precision is necessary as Dublin Core™ is deployed in the context of inference engines and ontology-based solutions. As of the time of writing, the DCMI Usage Board is considering the assignment of formal domains and ranges which make explicit the meanings intended in natural-language definitions [DOMAINS].
Literal values of properties without Literal ranges
For most DCMI metadata terms, the process of clarifying domains and ranges machine-understandably is straightforward and unambiguous. However, one problem with regard to legacy metadata usage is serious enough to bear closer scrutiny. The Dublin Core™ community has long distinguished between Simple and Qualified Dublin Core™ -- a distinction reflected in the difference between the specifications "Expressing Simple Dublin Core™ in RDF/XML" [DCMES-XML] and the "Expressing Qualified Dublin Core™ in RDF/XML" [DCQ-RDF-XML].
The two legacy specifications differ with regard to whether properties such as dc:creator and dc:date have values that are non-literal resources (e.g., a Person or a Date, seen as entities), or strings representing the resources (i.e., a value string). In "Expressing Simple Dublin Core™ in RDF/XML", a dc:creator is a name:
<http://www.example.com> dc:creator "John Smith".
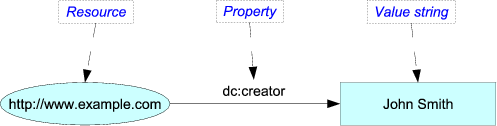
In "Expressing Qualified Dublin Core™ in RDF/XML", in contrast, a dc:creator is an entity, as in:
<http://www.example.com> dc:creator <http://www.example.org/person32>
or
<http://www.example.com> dc:creator _:xxx .
_:xxx rdf:type foaf:Person
_:xxx dcrdf:valueString "John Smith"
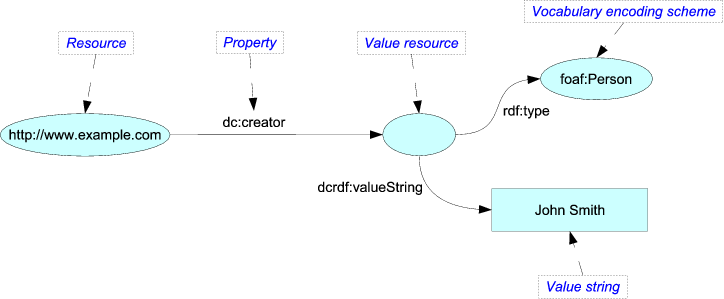
The new specification follows the latter approach -- dc:creator refers to an entity which can be identified (e.g., in an authority file) and described in its own right (e.g., with a name, an affiliation, and a birth date). The English-language definitions of these terms bear out this interpretation: dc:creator is "an entity primarily responsible for making the content of the resource", examples being "a person, an organization, or a service". However, the usage comments associated with these definitions also reflect the ambiguity: "Typically, the name of a Creator should be used to indicate the entity".
In accordance with the current approach, the DCMI Usage Board is considering the assignment of a range of "Agent" to dc:creator and dc:contributor, where "Agent" would be defined as "the class of all things that are a Person, Organization, or Service". Similarly, appropriate ranges would be specified for the other DCMI terms as well, with the same kinds of consequences for legacy Dublin Core™ metadata expressed in RDF. If used at all, the range "Literal" would apply only to metadata terms which are typically associated with value strings, such as dc:title.
In most cases, the appropriate range of a term has become reasonably obvious through a decade of implementation practice. In the cases of dc:creator and dc:contributor, however, that usage has been ambiguous, so the assignment of any specific range would make one or another part of the legacy metadata appear invalid in the context of machine processing. Declaring "Agent" as the range of dc:creator would mean that inferencing applications would expect to treat the value of the dc:creator property as a non-literal entity. Where legacy metadata represents names as literal values for dc:creator, applications would need to treat these as "special cases" in order to merge them with metadata in which those names were associated with the expected non-literal entity constructs.
The legacy specifications did not properly address these ambiguities, with the result that an unknown amount of Dublin Core-based RDF data is inconsistent with the definitions of the Dublin Core™ properties. The clarification of these ambiguities through the assignment of domains and ranges is currently considered to be a desirable step towards ensuring the long-term viability of Dublin Core™ in RDF.
Impact on legacy Dublin Core™ metadata
The declaration of domains and ranges for DCMI properties has important implications for the interpretation of legacy Dublin Core™ metadata in RDF. However, the interpretation of Dublin Core™ metadata in other formats, such as HTML [DCQ-HTML] and XML [DC-XML-GUIDELINES, [DC-XML], would not be negatively affected by these developments. The rules for interpreting metadata in these syntaxes in terms of the DCAM are simpler than for RDF, as these other syntaxes are not bound by the semantics of RDF.
The declaration of domains and ranges would help clarify the formal semantics of DCMI properties. Metadata creators would need to use syntactic constructs to ensure that RDF-consuming applications correctly interpret any value strings. The generation of Dublin Core™ metadata in RDF would become slightly more complex for anyone producing metadata by hand. However, these measures would eliminate the current ambiguity, enabling metadata that is mappable more consistently to the DCAM. Support by tools would be improved by the machine-processable restrictions. In order to process legacy metadata, metadata consumers might need to "special-case" any metadata containing value strings associated directly with the affected Dublin Core™ properties (i.e., without intervening non-literal nodes).
4. Support for value strings
The May 2006 Working Draft differs from the legacy specifications in its handling of value strings.
Support for multiple value strings
The DCAM specifies that each value can be represented in a DCAM statement by multiple value strings. The new RDF expression supports this construct, using thedcrdf:valueString property, a sub-property ofrdf:value. This allows value strings in different languages or using different syntax encoding schemes to be used as representations of a single value.
Deprecated use of rdfs:label and rdf:value
Value strings are now expressed using a new property dcrdf:valueString, a sub-property ofrdf:value with a range of rdfs:Literal. The use of rdfs:label or rdf:value for expressing value strings is no longer supported, as their original definitions do not clearly fit this purpose. Of course, the use of those properties is not forbidden, but these properties are not considered to have any special interpretation in terms of the DCAM.
Support for RDF datatypes
RDF datatypes can now be used with value strings, corresponding to the DCAM concept of Syntax Encoding Schemes.
For value strings occurring as the object of adcrdf:valueString property, this is a simple matter.
The new specification also allows the use of datatyped literals as direct values of properties under a specific set of conditions, namely: when the type (i.e., the vocabulary encoding scheme) of the actual value is an RDF datatype or equals rdfs:Literal. This preserves the correct semantics without ambiguity while still allowing for literal values of properties.``
5. Deprecated constructs
The May 2006 deprecates several constructs described in the May 2002 specification [DCQ-RDF-XML].
Deprecated use of RDF Containers
The RDF Container constructs rdf:Bag,rdf:Alt and rdf:Seq are no longer provided as an alternative for constructing ordered and unordered sets. They have no correspondence in the DCAM, and except in the case when the range of a property includes one of these classes, they should no longer be used.
Deprecated construct "poor-man's structured values"
The recursive use of rdf:value for structured values has been deprecated. It has no correspondance in the DCAM and does not lend itself very well to automated processing. The use of this construct is therefore no longer supported.
Note that the property used for value strings,dcrdf:valueString has a range ofrdfs:Literal and cannot therefore be used recursively.
Deprecated construct "poor-man's language qualification"
The use of "poor-man's language qualification" in the 2002 specification does not fit the DCAM and does not take into account the language tagging of plain literals in RDF. It is no longer supported.
6. Other changes
Clarification of the use of dc:identifier
In the deprecated recommendations, there is some ambiguity regarding the use of the dc:identifier property. As the value of the dc:identifier property is the actual identifier, the identifier should be referenced literally, i.e. using a literal string, as in
<http://example.org> dc:identifier "doi:blabla"^^<http://purl.org/dc/terms/URI>
or similar.
Removal of references to "dumb-down"
The dumb-down algorithm is independent of any particular expression of Dublin Core™ metadata (such as Dublin Core™ metadata in RDF) and is therefore defined in the DCMI Abstract Model. References to dumb-down have been removed from the text of the May 2006 Working Draft.
Removal of reification from the Working Draft
The use of reification is now considered to fall outside the scope of the specification and is therefore no longer part of the May 2006 Working Draft. As it does not interfere with the metadata itself, however, reification can still be used in accordance with RDF specifications.
Removal of RDF schemas from the Working Draft
The RDF schemas for DCMI properties and classes are part of the definitions of these terms and do not belong specifically to the RDF expression of Dublin Core™ metadata. They have been removed from the draft specification itself and can be accessed at http://dublincore.org/schemas/rdfs/.
References
- ABSTRACT-MODEL
- DCMI Abstract Model
<http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/abstract-model/> - DCMES-XML
- Expressing Simple Dublin Core™ in RDF/XML
<http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dcmes-xml/> - DCQ-RDF-XML
- Expressing Qualified Dublin Core™ in RDF/XML
<http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dcq-rdf-xml/> - DCQ-HTML
- Expressing Dublin Core™ in HTML/XHTML meta and link elements
<http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dcq-html/> - DC-ARCHITECTURE
- DCMI Architecture Working Group
<http://dublincore.org/groups/architecture/> - DC-ARCHITECTURE-LIST
- DCMI Architecture Working Group mailing list
<http://www.jiscmail.ac.uk/lists/dc-architecture.html> - DC-RDF
- Expressing Dublin Core™ metadata using the Resource Description Framework (RDF)
<http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dc-rdf/2006-05-29/> - DC-XML
- Expressing Dublin Core™ metadata using XML
<http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dc-xml/> - DC-XML-GUIDELINES
- Guidelines for implementing Dublin Core™ in XML
<http://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dc-xml-guidelines/> - DOMAINS
- DC property domains and ranges
<http://dublincore.org/usageboardwiki/PropertyDomainsAndRanges>
