Description Set Profiles: A constraint language for Dublin Core™ Application Profiles
| Creators: |
Mikael Nilsson
KMR Group, NADA, KTH (Royal Institute of Technology), Sweden |
| Date Issued: | 2008-03-31 |
| Latest Version: | https://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dc-dsp/ |
| Release History: | https://dublincore.org/specifications/dublin-core/dc-dsp/release_history/ |
| Description: | This specification describes an information model and XML expression of a "Description Set Profile" (DSP). A DSP describes structural constraints on a description set, allowing for formal expression of the constraints of a Dublin Core Application Profile. |
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Basic structure
- Basic semantics
- Usage examples
- Description Templates
- Statement templates
- XML structure
- RDF variant
- Examples
1. Introduction
The DCMI Description Set Profile specification describes an information model and XML expression of a "Description Set Profile" (DSP). The term description set and the associated concepts used in this specification are defined as in the DCMI Abstract model [DCAM].
A DSP is a way of describing structural constraints on a description set. It constrains the resources that may be described by descriptions in the description set, the properties that may be used, and the ways a value surrogate may be given.
A DSP can be used for many different purposes, for example:
- as a formal representation of the constraints of a Dublin Core™ Application Profile
- as configuration for databases
- as configuration for metadata editing tools
A DSP does not address the following:
- Human-readable documentation.
- Definition of vocabularies.
- Version control.
A DSP contains the formal syntactic constraints only, and will need to be combined with human-readable information, usage guidelines, version management, etc. in order to be used as an application profile. However, the design of the DSP information model is intended to facilitate the merging of DSP information and external information of the above kinds, for example by tools generating human-readable documentation for a Dublin Core™ Application Profile.
A Dublin Core™ Application Profile is a document, or set of documents, that puts a Description Set Profile into a broader context of Functional Requirements, Domain Models, guidelines on syntax and usage, and possibly data formats. See the Singapore Framework for Dublin Core™ Application Profiles for the broader picture.
2. Basic structure
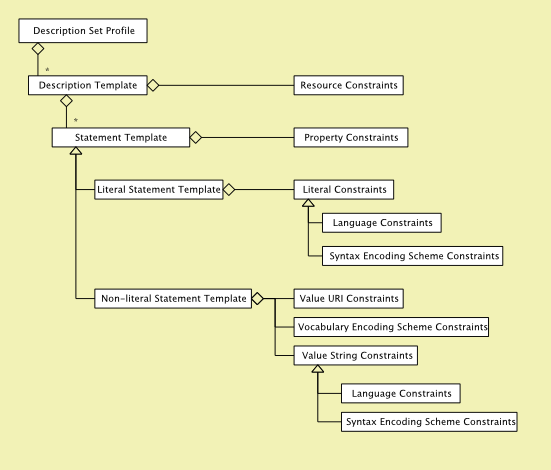
A DSP describes the structure of a Description Set by using the notions of "templates" and "constraints". A template describes the possible metadata structures in a conforming record.
There are two levels of templates in a Description Set Profile:
-
Description templates , which contain the statement templates that apply to a single kind of description as well as constraints on the described resource.
-
Statement templates , which contain all the constraints on the property, value strings, vocabulary encoding schemes, etc. that apply to a single kind of statement.
While templates are used to express structures, constraints are used to limit those structures. The following figure depicts the basic elements of the structure.
3. Basic semantics
The fundamental usage model for a DSP is to examine whether a metadata record matches the DSP.
Matching of a description set is defined as follows:
- Each description is bound to a Description Template by evaluating the Resource Constraint of each Description Template against the described resource. Each description must be bound to exactly one Description Template.
- For each description, each statement is bound to a Statement Template in the corresponding Description Template by evaluating the Property Constraint. Each statement must be bound to exactly one Statement Template.
- Evaluating constraints
- Now that all metadata in the description set has been bound to a template, all constraints can be verified.
- DescriptionTemplate
- A string that can be used in a Value Constraint to reference a description template that applies to the value resource.
- Allowed values
- A valid XML ID string.
- Default
- N/A
- XML Attribute Name
-
ID
- Whether descriptions matching this template are allowed to occur standalone, i.e. without being the value of a property.
- Allowed values
- "yes" / "no" / "both"
- Default
-
"both"
- Conditions
-
If standalone is "yes", a matching description may not be a description of value occurring elsewhere in the DSP.
If standalone is "no", a matching description *must* be a description of value occurring elsewhere in the DSP.
If standalone is "both", both are allowed.
If this description template is referred to in a Value Constraint, standalone cannot be "yes". - XML Attribute Name
- standalone
- The minimum number of times this kind of description must appear in the Description Set.
- Allowed values
- non-negative integer
- Default
- 0
- Conditions
- must be equal or less than the Maximum occurrence
- XML Attribute Name
- minOccurs
- The maximum number of times this kind of description is allowed to appear in the Description Set.
- Allowed values
- non-negative integer or "infinity"
- "infinity"
- Conditions
- must be equal or greater than the Minimum occurrence
- XML Attribute Name
- maxOccurs
- Classes that the resource may be an instance of
- Allowed values
- a list of class URIs
- Default
-
no constraint
- Conditions
- if given, the resource must be an instance of one of the given classes.
- XML Element Name
- ResourceClass
- StatementTemplate
- The minimum number of times this kind of statement must appear in the enclosing Description.
- Allowed values
- non-negative integer
- Default
-
0
- Conditions
- must be equal or less than the Maximum occurrence
- XML Attribute Name
- minOccurs
-
The maximum number of times this kind of statement is allowed to appear in the enclosing Description.
- Allowed values
- non-negative integer or "infinity"
- Default
- "infinity"
- Conditions
- must be equal or greater than the Minimum occurrence
- XML Attribute Name
- maxOccurs
- The type of value surrogate (literal/non-literal) that is allowed in this Statement.
- Allowed values
- "literal" / "nonliteral"
- Default
- both allowed
- Conditions
- If no value is given, no further constraining on the value surrogate can be made.
- XML Attribute Name
- type
-
By giving an explicit list of allowed properties
-
By requiring the property to be a sub-property of a given property.
- A set of properties that are allowed in this statement template.
- a list of property URIs
- Default
- N/A
- Conditions
- cannot occur together with a sub-property constraint
- XML Element Name
- Property
- Only sub-properties of the given property are allowed in this statement template. Note that the given property is included in this list (all properties are sub-properties of themselves).
- Allowed values
-
a property URI
- Default
- N/A
- Conditions
- cannot occur together with a property list constraint
- XML Element Name
- SubPropertyOf
- XML Element Name
- LiteralConstraint
- Literals that are allowed as values.
- Allowed values
- a list of literals, i.e. (string, language tag) or (string, syntax encoding scheme URI) pairs.
- no constraint
- Conditions
- if given, no other literal constraint may be given
- XML Element Name
- LiteralOption
- Whether languages are allowed for the literal
- Allowed values
- "mandatory" / "optional" / "disallowed"
- Default
-
"optional"
- Conditions
- if "mandatory", Syntax encoding schemes are automatically disallowed.
- XML Element Name
- LanguageOccurrence
-
Languages allowed for the literal
- Allowed values
- a list consisting of language tags
- Default
- no constraint
- XML Element Name
- Language
- Whether Syntax Encoding Scheme are allowed for the literal
- Allowed values
- "mandatory" / "optional" / "disallowed"
- Default
- "optional"
- Conditions
- if "mandatory", language tags are automatically disallowed.
- XML Element Name
- SyntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence
- Syntax encoding schemes allowed for the literal
- Allowed values
- a list consisting of syntax encoding scheme URIs
- no constraint
- XML Element Name
- SyntaxEncodingScheme
- XML Element Name
- NonLiteralConstraint
- A reference to a description template that may be used to describe the value
- an identifier defined in a Description Template
- Default
- Related description not allowed
- Conditions
- if given, any related description of the value within the record must match the referenced Description Template. If the referenced Description Template contains mandatory Statement templates, such a description of the value must exist.
- XML Attribute Name
- descriptionTemplateRef
- Classes that the value may be an instance of
- Allowed values
-
a list of class URIs
- Default
- no constraint
- Conditions
- if given, the value must be an instance of one of the given classes.
- XML Element Name
- ValueClass
- Whether a value URI must be given
- "disallowed" / "optional" / "mandatory"
- Default
- "optional"
- Conditions
- XML Element Name
- ValueURIOccurrence
- URIs that are allowed as value URIs.
- Allowed values
-
a list of URIs
- Default
- no constraint
- Conditions
- If a value URI is given, it must be taken from this list. Cannot be specified if value occurrence is "disallowed"
- XML Element Name
- ValueURI
- Whether a vocabulary encoding scheme must be given
- Allowed values
-
"disallowed" / "optional" / "mandatory"
- Default
- "optional"
- Conditions
- XML Element Name
- VocabularyEncodingSchemeOccurrence
- URIs that are allowed as Vocabulary Encoding schemes.
- Allowed values
- a list of URIs
- Default
- no constraint
- Conditions
- If a vocabulary encoding scheme is given, it must be taken from this list. Cannot be specified if vocabulary encoding scheme occurrence is "disallowed"
- XML Element Name
- VocabularyEncodingScheme
- ValueStringConstraint
- The minimum number of times this kind of value string must appear in the enclosing Statement.
- non-negative integer
- Default
- 0
- Conditions
- must be equal or less than the Maximum occurrence
- XML Attribute Name
- minOccurs
- The maximum number of times this kind of value string is allowed to appear in the enclosing Statement.
- Allowed values
-
non-negative integer or "infinity"
- Default
- "infinity"
- Conditions
- must be equal or greater than the Minimum occurrence
- XML Attribute Name
- maxOccurs
<dt> Binding of descriptions to description templates</dt>
<dt> Binding of statements to statement templates</dt>
</dl>
4. Usage examples
4.1. Example 1: Constraining the resource
The following DSP matches descriptions with a single resource. The resource must be an instance of foaf:Person.
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<DescriptionSetTemplate xmlns="http://dublincore.org/xml/dc-dsp/2008/03/31" >
<DescriptionTemplate ID="person" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" standalone="yes">
<ResourceClass>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person</ResourceClass>
</DescriptionTemplate>
</DescriptionSetTemplate>
As it stands, this DSP does not allow for the description of that resource to contain any statements, so it is not very useful.
4.2. Example 2: Constraining a property
The following DSP adds a mandatory foaf:name property with a literal value to the previous example.
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<DescriptionSetTemplate xmlns="http://dublincore.org/xml/dc-dsp/2008/03/31">
<DescriptionTemplate ID="person" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" standalone="yes">
<ResourceClass>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person</ResourceClass>
<StatementTemplate minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" type="literal">
<Property>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name</Property>
</StatementTemplate>
</DescriptionTemplate>
</DescriptionSetTemplate>
4.3. Example 3: Constraining the value
The following DSP constrains the value to be a literal without a language.
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<DescriptionSetTemplate xmlns="http://dublincore.org/xml/dc-dsp/2008/03/31">
<DescriptionTemplate ID="person" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" standalone="yes">
<ResourceClass>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person</ResourceClass>
<StatementTemplate minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" type="literal">
<Property>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name</Property>
<LiteralConstraint>
<LanguageOccurrence>disallowed</LanguageOccurrence>
</LiteralConstraint>
</StatementTemplate>
</DescriptionTemplate>
</DescriptionSetTemplate>
4.4. Example 4: Two resources
The following DSP allows for two kinds of resources: a single "document", and multiple "authors". The Person resources may only occur as values of the dcterms:creator property, not stand-alone. The value may only be described in a separate description with a mandatory foaf:name property.
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<DescriptionSetTemplate xmlns="http://dublincore.org/xml/dc-dsp/2008/03/31">
<DescriptionTemplate ID="document" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" standalone="yes">
<ResourceClass>http://purl.org/dc/terms/Text</ResourceClass>
<StatementTemplate minOccurs="1" type="nonliteral">
<Property>http://purl.org/dc/terms/creator</Property>
<NonLiteralConstraint descriptionTemplateID="person">
<ValueURIOccurrence>disallowed</ValueURIOccurrence>
<VocabularyEncodingSchemeOccurrence>disallowed</VocabularyEncodingSchemeOccurrence>
<ValueStringConstraint maxOccur="0"/>
</NonLiteralConstraint>
</StatementTemplate>
</DescriptionTemplate>
<DescriptionTemplate ID="person" standalone="no">
<ResourceClass>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person</ResourceClass>
<StatementTemplate minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" type="literal">
<Property>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name</Property>
<LiteralConstraint>
<LanguageOccurrence>disallowed</LanguageOccurrence>
</LiteralConstraint>
</StatementTemplate>
</DescriptionTemplate>
</DescriptionSetTemplate>
5. Description Templates
A description Template has the following attributes.
<dt> XML Element Name</dt>
</dl>
5.1. Identifier
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
5.2. Standalone
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
5.3. Minimum occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
5.4. Maximum occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
<dt> Default</dt>
</dl>
5.5. Resource Class Membership Constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6. Statement templates
A statement template has the following possible constraints.
<dt> XML Element Name</dt>
</dl>
6.1. Minimum occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.2. Maximum occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.3. Type constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
Note: that the type constraint should follow any range given for the used properties.
6.4. Property constraints
There are two ways of constraining the property in a statement:
Exactly one of the above methods must be used in a single statement template.
6.4.1. Property list constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
<dt> Allowed values</dt>
</dl>
6.4.2. Sub-property constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.5. Literal value constraints
Constrains a literal value surrogate in a statement. Only allowed in the case that the type constraint has the value "literal".
6.5.1. Literal list constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
<dt> Default</dt>
</dl>
6.5.2. Literal language constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.5.3. Literal language list constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.5.4. Syntax Encoding Scheme constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.5.5. Syntax Encoding Scheme list constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
<dt> Default</dt>
</dl>
6.6. Non-literal value constraints
Constrains the value surrogate in a statement. Only allowed in the case that the type constraint has the value "nonliteral".
6.6.1. Description template reference
<dt> Summary</dt>
<dt> Allowed values</dt>
</dl>
6.6.2. Class membership constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
Note: this is not a syntactic constraint, and as such might not be evaluated by all processors. If a type statement is desired, an explicit Statement template in a Description Template for the value resource should be created.
6.6.3. Value URI constraint
6.6.3.1. Value URI occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
<dt> Allowed values</dt>
</dl>
6.6.3.2. Value URI list constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.6.4. Vocabulary encoding scheme constraint
6.6.4.1. Vocabulary encoding scheme occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.6.4.2. Vocabulary encoding scheme list constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.6.5. Value String Constraints
If at least one value string constraint is given, any value string must match at least one of the constraints. If no value string constraint is given, any value string is allowed.
For each value string constraint, the following may be specified.
<dt> XML Element Name</dt>
</dl>
6.6.5.1. Minimum occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
<dt> Allowed values</dt>
</dl>
6.6.5.2. Maximum occurrence constraint
<dt> Summary</dt>
</dl>
6.6.5.3. Other constraints
All Literal value constraints (section 6.5) can be used for value strings as well.
7. XML structure
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<DescriptionSetTemplate>
<DescriptionTemplate standalone="" ID="" minOccurs="" maxOccurs="">
<ResourceClass></ResourceClass>
<ResourceClass></ResourceClass>
<StatementTemplate ID="" minOccurs="" maxOccurs="" type="">
<Property></Property>
<Property></Property>
<SubPropertyOf></SubPropertyOf>
<NonliteralConstraint descriptionTemplateRef="">
<ValueClass></ValueClass>
<ValueClass></ValueClass>
<ValueURIOccurrence></ValueURIOccurrence>
<ValueURI></ValueURI>
<ValueURI></ValueURI>
<VocabularyEncodingSchemeOccurrence></VocabularyEncodingSchemeOccurrence>
<VocabularyEncodingScheme></VocabularyEncodingScheme>
<VocabularyEncodingScheme></VocabularyEncodingScheme>
<ValueStringConstraint minOccurs="" maxOccurs="">
<LiteralOption lang="" SES=""></LiteralOption>
<LiteralOption lang="" SES=""></LiteralOption>
<LanguageOccurrence></LanguageOccurrence>
<Language></Language>
<Language></Language>
<SyntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence></SyntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence>
<SyntaxEncodingScheme></SyntaxEncodingScheme>
<SyntaxEncodingScheme></SyntaxEncodingScheme>
</ValueStringConstraint>
</NonLiteralConstraint>
<LiteralConstraint>
<LiteralOption lang="" SES=""></LiteralOption>
<LiteralOption lang="" SES=""></LiteralOption>
<LanguageOccurrence></LanguageOccurrence>
<Language></Language>
<Language></Language>
<SyntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence></SyntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence>
<SyntaxEncodingScheme></SyntaxEncodingScheme>
<SyntaxEncodingScheme></SyntaxEncodingScheme>
</LiteralConstraint>
</StatementTemplate>
</DescriptionTemplate>
</DescriptonSetTemplate>
8. RDF variant
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:dsp="http://purl.org/dc/dsp/">
<dsp:DescriptionTemplate rdf:about="#d1">
<dsp:standalone rdf:datatype="xsd:boolean">true</dsp:standalone>
<dsp:minOccur rdf:datatype="xsd:nonNegativeInteger">0</dsp:minOccur>
<dsp:maxOccur rdf:datatype="xsd:nonNegativeInteger">0</dsp:maxOccur>
<dsp:resourceClass rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:resourceClass rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:statementTemplate>
<dsp:LiteralStatementTemplate>
<dsp:minOccur rdf:datatype="xsd:nonNegativeInteger">0</dsp:minOccur>
<dsp:maxOccur rdf:datatype="xsd:nonNegativeInteger">0</dsp:maxOccur>
<dsp:property rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:property rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:subPropertyOf rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:literalConstraint>
<dsp:LiteralConstraint>
<dsp:literal xml:lang="" rdf:datatype=""></dsp:literal>
<dsp:literal xml:lang="" rdf:datatype=""></dsp:literal>
<dsp:languageOccurrence rdf:datatype="dsp:occurrence"></dsp:languageOccurrence>
<dsp:language rdf:datatype="xsd:language"></dsp:language>
<dsp:language rdf:datatype="xsd:language"></dsp:language>
<dsp:syntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence rdf:datatype="dsp:occurrence"></dsp:syntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence>
<dsp:syntaxEncodingScheme rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:syntaxEncodingScheme rdf:resource=""/>
</dsp:LiteralConstraint>
</dsp:literalConstraint>
</dsp:LiteralStatementTemplate>
</dsp:statementTemplate>
<dsp:statementTemplate>
<dsp:NonLiteralStatementTemplate>
<dsp:nonLiteralConstraint>
<dsp:NonLiteralConstraint>
<dsp:descriptionTemplate rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:valueClass rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:valueClass rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:valueURIOccurrence rdf:datatype="dsp:occurrence"></dsp:valueURIOccurrence>
<dsp:valueURI rdf:datatype="xsd:URI"></dsp:valueURI>
<dsp:valueURI rdf:datatype="xsd:URI"></dsp:valueURI>
<dsp:vocabularyEncodingSchemeOccurrence rdf:datatype="dsp:occurrence"></dsp:vocabularyEncodingSchemeOccurrence>
<dsp:vocabularyEncodingScheme rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:vocabularyEncodingScheme rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:valueStringConstraint>
<dsp:ValueStringConstraint>
<dsp:minOccur rdf:datatype="xsd:nonNegativeInteger">0</dsp:minOccur>
<dsp:maxOccur rdf:datatype="xsd:nonNegativeInteger">0</dsp:maxOccur>
<dsp:literal xml:lang="" rdf:datatype=""></dsp:literal>
<dsp:literal xml:lang="" rdf:datatype=""></dsp:literal>
<dsp:languageOccurrence rdf:datatype="dsp:occurrence"></dsp:languageOccurrence>
<dsp:language rdf:datatype="xsd:language"></dsp:language>
<dsp:language rdf:datatype="xsd:language"></dsp:language>
<dsp:syntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence rdf:datatype="dsp:occurrence"></dsp:syntaxEncodingSchemeOccurrence>
<dsp:syntaxEncodingScheme rdf:resource=""/>
<dsp:syntaxEncodingScheme rdf:resource=""/>
</dsp:ValueStringConstraint>
</dsp:valueStringConstraint>
</dsp:NonLiteralConstraint>
</dsp:nonLiteralConstraint>
</dsp:NonLiteralStatementTemplate>
</dsp:statementTemplate>
</dsp:DescriptionTemplate>
</rdf:RDF>
9. Examples
9.1 "Simple" Dublin Core™
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<DescriptionSetTemplate xmlns="http://dublincore.org/xml/dc-dsp/2008/03/31">
<DescriptionTemplate>
<StatementTemplate>
<Property>http://purl.org/dc/terms/title</Property>
</StatementTemplate>
<StatementTemplate>
<Property>http://purl.org/dc/terms/creator</Property>
</StatementTemplate>
<!-- etc -->
</DescriptionTemplate>
</DescriptionSetTemplate>
9.2 Simple FOAF
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<DescriptionSetTemplate xmlns="http://dublincore.org/xml/dc-dsp/2008/03/31" >
<DescriptionTemplate ID="person" minOccur="1" maxOccur="1">
<ResourceClass>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person</ResourceClass>
<StatementTemplate minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" type="literal">
<Property>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name</Property>
</StatementTemplate>
<StatementTemplate type="nonliteral">
<Property>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/knows</Property>
<NonLiteralConstraint descriptionTemplateRef="person">
<ValueClass>http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person</ValueClass>
</NonLiteralConstraint>
</StatementTemplate>
<!-- etc -->
</DescriptionTemplate>
</DescriptionSetTemplate>
2014-10-26: See also dcmi-dsp.xsd.
